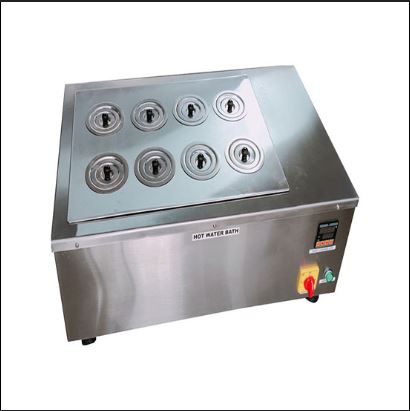

A "water bath" can refer to either a laboratory device for precise temperature control or a home canning technique. In a
Read More

"Deep freeze" can refer to a cold storage appliance for food, a pain-relief product for injuries, or a computer protecti
Read More

An autoclave is a machine that uses steam under pressure to sterilize equipment and materials by killing microorganisms,
Read More

Laboratory machine with two stacked platforms that performs a circular, orbital shaking motion to mix samples
Measuring EMF field monitor beserta E-field 100kHz-6GHz, E-field 3MHz-18GHz dan ELF probe (Elektrik &Magnetik) 5Hz-100kH
Read More
TRANSCIEVER ELECTROMAGNETIC CELL / ANRITSU/MG 32692C. sistem kalibrasi dan pengukuran frekuensi radio. Ia adalah sistem
Read More
Measure radiofrequency and microwave electric field strength from 75MHz up to 3GHz. Measure radiofrequency and microwave
Read More
Signal Generator yang menjadi sebahagian dari sistem GTEM Cell bagi menjana Radiofrequency di Makmal RF NIR. Generating
Read More
The system is used to freezedry/lyophilize the radiopharmaceutical kits. The software is used to control the freezedryin
Read More
Acoustic Televiewer.
GAMMA SPECTROMETER.
High Energy electron microscope.
Physical N Mechanical Characterization/Testing.
Polymer melt blending machine.
Determination, measurement and identification of chemicals and functional groups.
%booking_description%